Search Results
Results for: 'intestinal cell erosion'
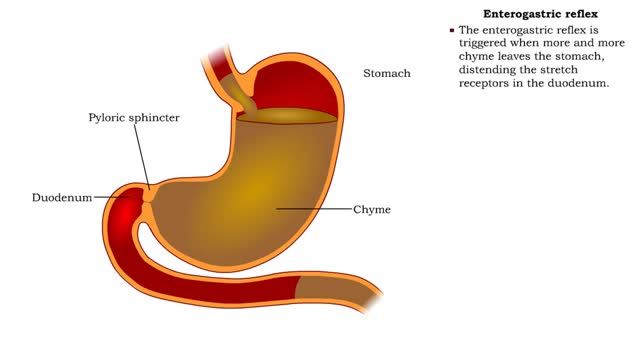
Stomach peristalsis & Enterogastric reflex
By: HWC, Views: 6062
• Food enters, distending the stomach. • Stretch receptors activate enteric reflexes that promote peristaltic movements. • These movements, called mixing waves, begin to mix the food with stomach secretions. • Mixing waves force the digesting food (chyme) toward and through the pylo...
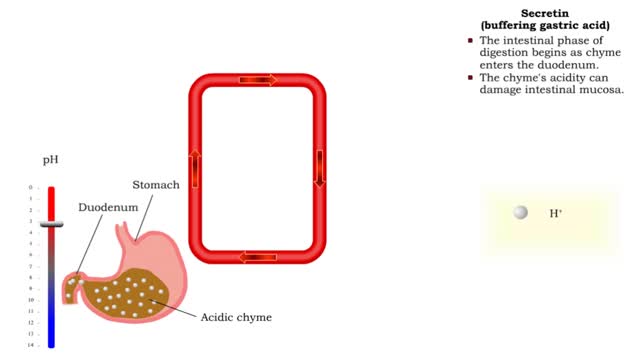
Gastrin (gastric emptying) & Secretin (buffering gastric acid)
By: HWC, Views: 6202
• Gastrin also binds to the smooth muscle cells in the stomach causing: • Increased gastric motility. • Opening of pyloric sphincter. • Increased gastric emptying. • The intestinal phase of digestion begins as chyme enters the duodenum. • The chyme's acidity can damage int...
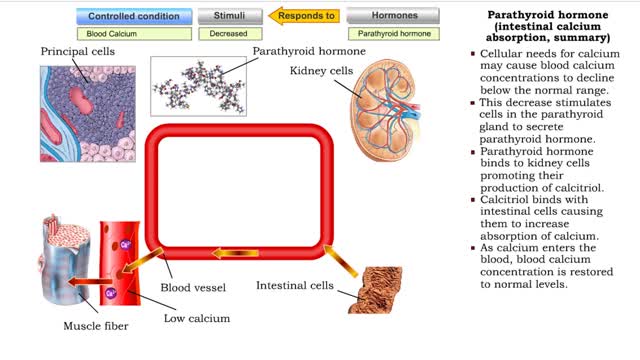
Parathyroid hormone (bone resorption) & Calcitonin (bone deposition)
By: HWC, Views: 6657
• Cellular needs for calcium may cause blood calcium concentrations to decline below the normal range. • This decrease stimulates cells in the parathyroid gland to secrete parathyroid hormone. • Binding of parathyroid hormone to osteoclasts in bone tissue promotes bone resorption and th...
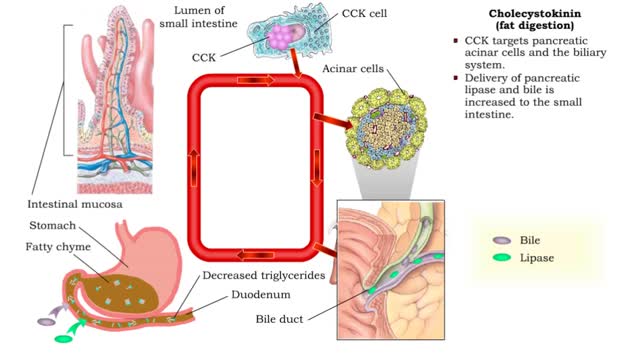
Secretin (inhibiting gastric acid secretion), Cholecystokinin (fat digestion) & Cholecystokinin
By: HWC, Views: 6389
• As chyme approaches the small intestine, secretin also targets acid-producing parietal cells in the gastric mucosa. • Increased secretin inhibits gastric add secretion. • With less gastric acid produced, the chyme going into the intestine is less acidic. • The hormone CCK also reg...
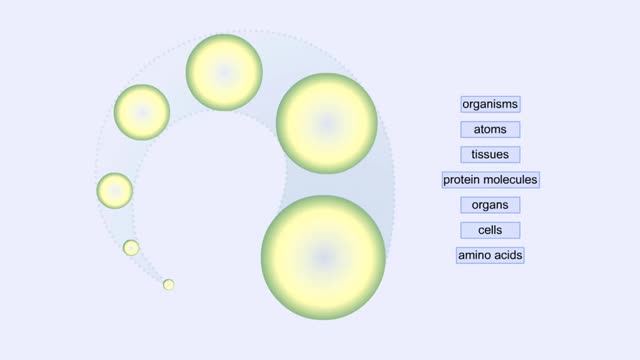
Proteins Defined, Hierarchy & Composition of Cells
By: HWC, Views: 6142
Proteins are long chains of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. Together with the other three biological macromolecules—carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids—proteins are the building blocks of cells. Proteins are the most complex and abundant biological macromolecules in cel...
Digestive chemicals - water, gastric acid, bile & bicarbonate
By: HWC, Views: 6350
• Water is the most abundant molecule in ingested fluids. • Water plays a primary role in hydrolytic digestive reactions. • Helps liquefy and transport digestive foodstuffs down the tract. • Transports secretions from accessory digestive organs to gastrointestinal tract. • Aids ...
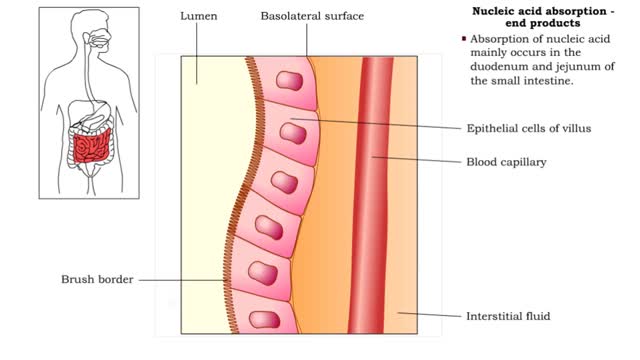
Nucleic acid digestion - brush border enzymes, end products & transport mechanism
By: HWC, Views: 6427
• Further digestion occurs at the microvilli (brush border) of the epithelial cells of the villi in the small intestine. • Two brush border enzymes complete nucleic acid digestion: • Phosphatases, which catalyze the cleavage of a phosphate to form a nucleoside (nitrogenous base and pent...
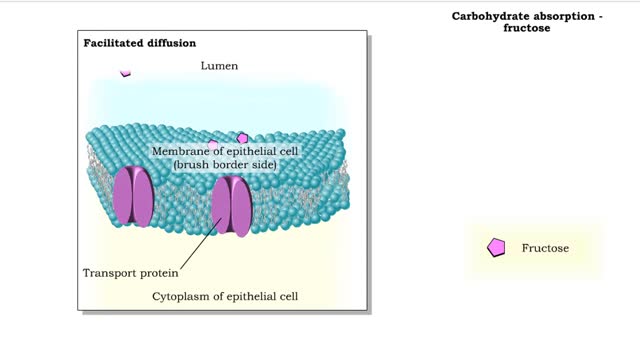
Carbohydrate digestion (brush border enzymes, end products) & Carb absorption (fructose, galactose)
By: HWC, Views: 6676
• Carbohydrate digestion concludes in microvilli of the small intestine, in brush border epithelial cells. Carbohydrate digestion -brush border enzymes • Four brush-border enzymes are involved: • Alpha-dextrinase breaks down alpha-dextrin chains by removing glucose units. • Sucras...
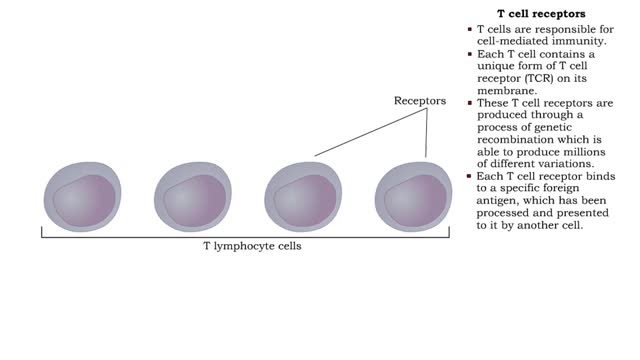
By: HWC, Views: 6337
• T cells are responsible for cell-mediated immunity. • Each T cell contains a unique form of T cell receptor (TCR) on its membrane. • These T cell receptors are produced through a process of genetic recombination which is able to produce millions of different variations. • Each T ce...
Advertisement